The filing of income tax return is a legal obligation of every individual whose total income during the previous year exceeds the maximum amount which is not chargeable (for more details for limit of each financial year refer Income Tax Rate / Slab) to income tax under the provisions of Income Tax Act, 1961. The return should be furnished in the prescribed form on or before the due date(s).
Usually Due date will be 31 July of assessment year for previous financial year. Individual can also file Income Tax Returns for previous assessment years as well.
How to File Income Tax Returns?
Income Tax Department has introduced a convenient way to file these returns online using the Internet with following steps (its totally free - no agent involved - Individual can do it easily):
- One time registration with valid PAN.
- Get the Excel Utility based on ITR form applicable.
- Fill the Excel, Validate and Generate the XML.
- Upload the XML, Get ITR-V (Receipt), Sign and send it to IT Dept.
Each steps explained in detailed description with screen shots.
One time registration required with valid PAN:
- If you didn't register with Income Tax E Filing site previously then open Income Tax India E Filing site - https://incometaxindiaefiling.gov.in and click on Register link.
- It will prompt PAN. Enter your PAN and click on Click Me button.
- It will check whether entered PAN is registered with Income Tax India E Filing site or not. If PAN already registered then it will display message: This PAN is already registered, If you forgot your password then click on Login link on main page of Income Tax India E Filing Site. It will open Member Login page, on this page click on Forget Password link to set new password. It will ask few details like PAN details, secret question or last E filing acknowledgement number and bank account number etc.
- If PAN is not registered, it will ask various details as displayed in below image:
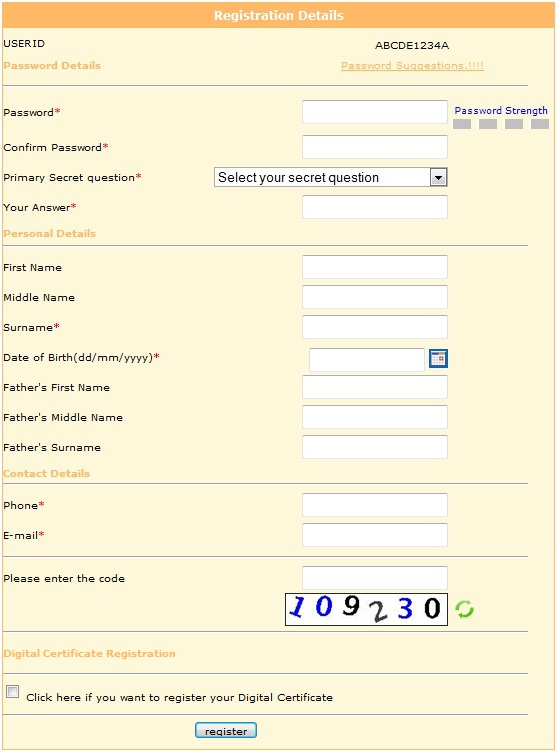
- Your PAN is your User ID for Income Tax India E Filing site.
- In future if you forget your password then you can set new password using Primary Secret Question.
- Please don't opt for Digital Certificate now only.
- Once you fill proper details click on Register button. You will get email from Income Tax India E Filing site on successful registration.
Get the Excel Utility based on ITR form applicable:
- Once you registered with Income Tax India E Filing site, click on Login link: Login using your PAN and password. After login site will be displayed as below:
- If you want to file Income Tax Return for current Assessment Year then move cursor to first option (e-Filing A.Y. ####-##) under DOWNLOAD and select Individual, HUF.
Note: Link title e-Filing A.Y. ####-## will be changed based on year. For example current assessment year is 2012-13 so link name is e-Filing A.Y. 2012-13 for next year it will be e-Filing A.Y. 2013-14 and so on.
- It will display page in which mappings between sources/details of income and ITR Form for Individual and HUF displayed and also link of excel utility for each ITR.
- Mapping of source of income and ITR displayed as below:
Note: Link title e-Filing A.Y. ####-## will be changed based on year. For example current assessment year is 2012-13 so link name is e-Filing A.Y. 2012-13 for next year it will be e-Filing A.Y. 2013-14 and so on.

- If your source of income is one of salary, pension, interest income or Family pension then you need to file ITR - 1 which is called as SAHAJ.
- Apart from above, if your source of income is from other sources, income/loss from house property, Capital gains/loss on sale of investments/property then you need to file only ITR - 2.
- Apart from above (ITR-2), if you are partner in a partnership firm then you need to file only ITR - 3.
- For other source of income see above mappings and check which ITR is required to file your Income Tax Return.
After finalizing ITR, download excel utility (which is zip file contains Excel and help file) for that ITR (from same page displayed after above mappings) as below:
- If you want to file Income Tax Return for previous Assessment Year then move cursor to second option (Previous Years) under DOWNLOAD and select appropriate Assessment Year. You can file Income Tax Return online from Assessment year 2006-07.
Fill the Excel, Validate and Generate the XML:
Most of individuals required ITR-1 to file Income Tax Return.
Prerequisite to Fill the ITR-1 Excel:- FORM - 16 received from employer & other deductors. For more details refer Understand FORM - 16
- Bank details
- Interest statements by bank FDs / NSC.
Extract the zip file (downloaded from Income Tax India E-Filing site) in one folder and Open the excel file. This excel contains macro so enable the macro in excel before editing the excel, for more details on how to enable macro in excel refer Enable Macro in Excel:
Fields marked with light green background color needs to be filled by Individual, all other fields are calculated automatically by excel. Excel has following sheets:
Income Details: Contains personal details (like Name, PAN, Address etc) and income details (which can be filled from FORM - 16). It has three important options (Validate, Calculate Tax and XML Generate).
Fill Personal details, Income details from FORM - 16 and Validate the sheet.
TDS: Contains Tax Deducted at Source by employer (which can be again filled from FORM - 16), from other deductors (in case of income other than salary) and Advance / Self Assessment tax payments.
Tax paid and Verification: Contains Tax payable, paid, refundable details. Also contains individual's bank details (in case to get refund from Income Tax Department) and declaration.
80G: Contains contribution of Individual towards section 80G. For more details about Section 80 G refer Section 80G.
Process to fill Excel, Validate & Generate XML:- Fill Personal Information, Filing Status, Income & Deduction in Income Details sheet and click on Validate button.
- Fill Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) details from FORM - 16 (in case of Salary and income other than Salary) in TDS sheet. Also fill the details of Advance Tax / Self Assessment Tax (if any) and click on Validate option.
- Fill third (Tax Paid and Verification) sheet and click on Validate option.
- Select the first (Income Details) sheet and click on Calculate Tax option.
- Check third (Tax paid & Verification) sheet - 18 Tax Payable (15-17), if it contains non zero value that means individual needs to pay that much tax to Income Tax Department.
- Pay this amount using NSDL site and mention details of tax payment information in TDS sheet under Advance Tax & Self Assessment Tax Payments section.
- If Tax Payable (15-17) in third (Tax paid & Verification) sheet is zero then click on XML Generate option in first (Income Details) sheet. It will create one sheet (Pre-XML Check) with Save XML button on it.
- Click on Save XML in Pre-XML Check sheet, it will save on the same path where Excel is located.
Upload the XML, Get ITR-V (Receipt), Sign and send it to IT Dept:
- Login on Income Tax India E Filing site using PAN and password.
- Move cursor / mouse on Select Assessment Year under SUBMIT RETURN option and select assessment year for which you want to file income tax return. It will display below options:
Select Form Name: ITR-1
Do you want to Digitally sign the File: No
Click on Next button
- It will prompt for XML file selection. Click on Choose File and select the XML file. Click on Upload button.
- After upload it will give link of ZIP file (which contains ITR-V). Download this zip file and open PDF from zip file (IT department will also email the same zip file on your email id which is mentioned in your profile).
PDF file is ITR-V Form. ITR-V FORM is password protected.Password will be your PAN and date of birth in ddmmyyyy format.
For example: PAN is ABCDE1234A and date of birth is 01-01-1987 then password will be abcde1234a01011987.
- Open the ITR-V FORM and verify it against excel / FORM - 16. It will look like below:
- Print this ITR-V FORM and sign in VERIFICATION section.
- Post / mail signed ITR-V FORM through Ordinary or Speed Post to the Income Tax Department on mentioned address within 120 days. Address will be as below:
Income Tax Department - CPC,
Post Bag No - 1,
Electronic City Post Office,
Bengaluru - 560100,
Karnataka.
ITR 1 Excel's Detailed description:
Income Details:
This sheet has mainly four sections as below: After filling all sections in this sheet click on Validate option.

- Personal Information: Contains various details like
Name - First Name, Middle Name, Last Name.
PAN.
Address (Gender (Male / Female)
Contact details (Email Address, Mobile No, Phone No.Status (I - Individual)Employer Category (Other / NA / GOV / PSU) - If Individual is not working then select NA. - FILING STATUS: Contains details
Income Tax Ward / Circle - Area / City where individual resides. No need to fill this, While validating / XML Generate will populate this field automatically.
Return Filed Under Section: 11 - Before Due Date (Due date is 31st July of assessment year).
12 - After Due Date
13 - In response to notice (u/s) under section 142(1).
14 - In response to notice under section 148.
15 - In response to notice under section 153A.
16 - In response to notice under section 153C.
17 - Revised return 139(5) - After filing return, if individual feels something is missing then this section is used.
18 - In response to notice under section 139(9) for removal of defects.
Original / Revised Return - Original - for first time. Revised in case of section 139(5) / 139(9).
In case of Revised Return provide Original Acknowledgement no & Date.
In case of u/s 139(9) Provide Original Acknowledgement No, Notice No and Notice date received from Income Tax Department.
Residential Status - Resident / Non-Resident / Resident but normally not resident.
Tax Status: Nil Tax Balance / Tax Payable / Tax Refundable.

- Income & Deductions: contains details same as FORM - 16 (these section filled using FORM - 16) as below:
1 Income from Salary / Pension (Ensure to fill Sch TDS1): Amount against INCOME CHARGEABLE UNDER THE HEAD "SALARIES" from FORM - 16 will come over here.
2 Income from one House Property: Amount against Income under the head Income from house property from FORM - 16 will come in this cell. If this amount is negative then put it as negative amount.
3 Income from Other Sources (Ensure to fill Sch TDS2): Sum of figure against Income under the head Income from Capital Gains & Income under the head Income from other sources will come in this section.
4 Gross Total Income (1 + 2 + 3): This is sum of above three kinds of income.
5 Deductions under Chapter VI A (Section): Fill the various sections (liek 80C, 80D, 80CCF, 80DD, 80DDB, 80E etc - except 80G) under this head from FORM - 16.
6 Deductions (Total of 5a to 5m): Sum of all deductions up to its limit. Automatically Excel will calculate.
7 Total Income (4 - 6): Gross Total Income - Total Deductions.
8 Tax Payable on Total Income: Clicking on Calculate Tax option will calculate Tax Payable based on income rate/ slab. Individual do not worry about this.
9 Education Cess, including Secondary and higher secondary cess on Tax Payable (8): Clicking on Calculate Tax option will calculate based on Tax Payable.
10 Total Tax, Surcharge and Education Cess (Payable) (8 + 9): Summation of Tax Payable, Education Cess, Secondary and higher secondary cess.
11 Relief under section 89: If individual gets relief under section 89 then enter amount.
12 Relief under section 90/91: If individual gets relief under section 89 then enter amount.
13 Balance Tax Payable (10 - 11 - 12): Total tax - relief under sections 89, 90/91. Calculate Tax option will calculate it.
14 Total Interest u/s 234A 234B 234C: Calculate Tax option will calcuate interest if Tax payable is more than paid tax. For this Fill the TDS sheet.
15 Total Tax and Interest Payable (13 + 14): Summation of Balance Tax Payable and Interest. It will be calculated automatically after click on Calculate Tax option.
TDS:
This sheet has mainly three sections as below: After filling all sections in this sheet click on Validate option.

- 23 Details of Tax Deducted at Source from SALARY [As per FORM 16 issued by Employer(s)]: Individual can fill this details from FORM - 16. Add details for each employer (if you have FORM - 16 from more than one employer). Provide TAN, Name of Employer, Income Chargeable under head salaries & Total Tax Deducted.
- 24 Details of Tax Deducted at Source on Income OTHER THAN SALARY [As per FORM 16 A issued by Deductor(s)]: For source of income other than salary and if tax deducted from that income then provide same details (TAN, Name of deductor, Unique TDS certificate No, Deducted Year, Total Tax deducted, Amount claimed this year) under this section.
- 25 Details of Advance Tax and Self Assessment Tax Payments: If individual paid any advance tax or self assessment tax then provide details over here. Like for example, employer deducted less tax and if employee want to pay actual tax then employee can pay the tax (in case of advance / self assessment tax).
While filling Income Tax Return, if individual finds he needs to pay more tax than actual paid then he can pay tax (along with interest calculated in 14 Total Interest u/s 234A, 234B, 234C mentioned in Income Details sheet) through NSDL site and provide details in this section and file the income tax return.
Calculation of pending tax (if any) = 15 Total Tax and Interest Payable [from Income Details sheet] - ( sum of Total Tax Deducted [from TDS sheet] + sum of Amount out of claimed this year [from TDS sheet] ). Individual needs to pay same amount as Self Assessment Tax.
Tax Paid and Verification:
This sheet has mainly three sections as below: After filling all sections in this sheet click on Validate option.
- Taxes Paid:
16 Taxes Paid: These fields are calculated automatically once click on Calculate Tax on Income Details sheet. Contains summary of taxes paid through various ways:16a Advance Tax (from item 25): It contains summation of advance tax entered in previous sheet (TDS) under Details Advance Tax and Self Assessment Tax Payments. This excel will identify whether its advance tax or Self Assessment.16b TDS (Total from item 23 + item 24): Contains total tax deducted as source (TDS) from previous sheet. Its sum of TDS on Salary and TDS on Income other than Salary.16c Self Assessment Tax (item 25): Contains Tax paid by individual as Self Assessment during assessment year (not during financial year). This amount is inclusive of interest (which is calculated u/s 234A, 234B and 234C).
17 Total Taxes Paid (16a+16b+16c): Sum of Advance Tax, TDS and Self Assessment Tax.
18 Tax Payable (15-17) (if 15 is greater than 17): This explains whether individual needs to pay more taxes or not. 15 Total Tax and Interest Payable [from Income Details sheet] - 17 Total Taxes Paid [from this sheet].
If this amount is greater than zero then individual needs to pay this amount to Income Tax of department as part of Income Tax.
If this amount is zero then exact income tax is paid by individual, there is nothing due. - Refund:
19 Refund (17-15) if 17 is greater than 15: This explains individual will get refund from Income Tax Department. 17 Total Taxes Paid [from this sheet] - 15 Total Tax and Interest Payable [from Income Details sheet].
To get refund from Income Tax Department individual needs to provide below details
20 Enter your Bank Account number: Provide bank account number which is single account on your name only.
21 Direct Deposit or Cheque: (Select Yes if you want your refund by direct deposit into your bank account, Select No if you want refund by Cheque)
22 In case of direct deposit to your bank account give additional detailsMICR Code: MICR code of bank branch, It will help Income Tax Department to deposit refund amount online.
Type of Account: Savings / Current. - 26 Exempt Income for reporting purpose only: Contains any income (agriculture income greater than 5000). Its used only for reporting purpose. There will be no income tax on it.
- Verification: Provide Name, Father Name, Date, Place and PAN number for verification purpose.
Pre-XML Check:
After validating all sheets, Click on Calculate Tax option on first (Income Details) sheet. Verify Tax Payable / Refundable. If everything is ok then click on XML Generate option in first sheet. It will create this sheet. Save XML option will be there on new sheet as below:
Click on Save XML option, it will save xml file on same path where ITR1 excel is located.










